blood, which are then excreted in your urine. When chronic kidney disease reaches an advanced stage, dangerous levels of fluid, electrolytes and wastes can build up in your body.
In the early stages of chronic kidney disease, you may have few signs or symptoms. Chronic kidney disease may not become apparent until your kidney function is significantly impaired.
Treatment for chronic kidney disease focuses on slowing the progression of the kidney damage, usually by controlling the underlying cause. Chronic kidney disease can progress to end-stage kidney failure, which is fatal without artificial filtering (dialysis) or a kidney transplant.
Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of chronic kidney disease develop over time if kidney damage progresses slowly. Signs and symptoms of kidney disease may include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- Fatigue and weakness
- Sleep problems
- Changes in how much you urinate
- Decreased mental sharpness
- Muscle twitches and cramps
- Swelling of feet and ankles
- Persistent itching
- Chest pain, if fluid builds up around the lining of the heart
- Shortness of breath, if fluid builds up in the lungs
- High blood pressure (hypertension) that's difficult to control
Signs and symptoms of kidney disease are often nonspecific, meaning they can also be caused by other illnesses. Because your kidneys are highly adaptable and able to compensate for lost function, signs and symptoms may not appear until irreversible damage has occurred.
Causes
Chronic kidney disease occurs when a disease or condition impairs kidney function, causing kidney damage to worsen over several months or years. Diseases and conditions that cause chronic kidney disease include:

- Type 1 or type 2 diabetes
- High blood pressure
- Glomerulonephritis (gloe-mer-u-low-nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the kidney's filtering units (glomeruli)
- Interstitial nephritis (in-tur-STISH-ul nuh-FRY-tis), an inflammation of the kidney's tubules and surrounding structures
- Polycystic kidney disease
- Prolonged obstruction of the urinary tract, from conditions such as enlarged prostate, kidney stones and some cancers
- Vesicoureteral (ves-ih-koe-yoo-REE-tur-ul) reflux, a condition that causes urine to back up into your kidneys
- Recurrent kidney infection, also called pyelonephritis (pie-uh-low-nuh-FRY-tis)
Risk factors
Factors that may increase your risk of chronic kidney disease include:
- Heart and blood vessel (cardiovascular) disease
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Being African-American, Native American or Asian-American
- Family history of kidney disease
- Abnormal kidney structure
- Older age
Renal Disease Ayurvedic Treatment
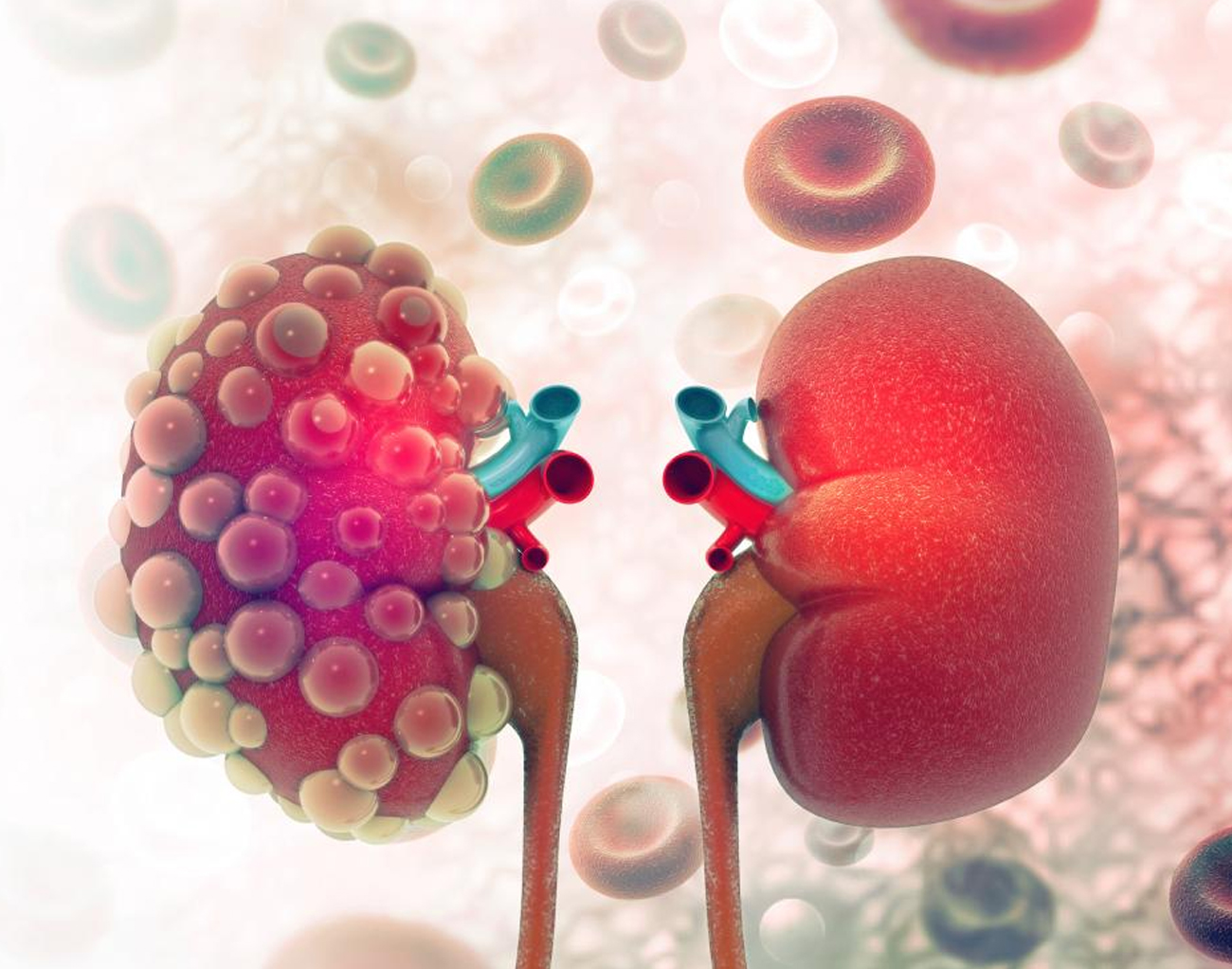
A person has two kidneys which are located near the middle of the back and just below the rib cage. Each kidney consists of millions of tiny filtration structure which are known as nephron. A nephron filters the blood and removes waste and extra water from it. All kidney diseases or disorders affect nephron and hence affects the filtration function of the kidneys. Ayurvedic medicine for kidney disease treatment work to remove such health disorders and kidney disease that affects the functions of the kidneys.
Ayurvedic medicines are safe and are away from every side effect. All the Ayurvedic medicine for kidney disease is made up of natural and unrefined herbs such as Varun, Punarnava, Kaasni etc. As ayurvedic medicines don’t consist of any drugs or antibiotics, hence it doesn’t increase the risk of any side effect for the patient.
At Kalam Ayurvedic Centre, more than 1000 kidney patients are getting served with Ayurvedic kidney treatment, who are now enjoying a disease-free life. We are providing risk-free treatment and Ayurvedic medicine for kidney which works for the elimination of root causes that are found to link with kidney disease.